Biggest Mistakes Beginners Make When Trading Option
Trading options can be an exciting venture, but it comes with its own set of risks. Mistakes mean losing money, and losing money can be painful. So, let’s dive into some of the biggest mistakes beginners make when trading options and how to avoid them.
Not Planning Your Trade
Planning is essential not just in trading but in life. Winging it may work for minor things, but when it comes to important matters, successful individuals always have a plan.
Options trading is like a battle between buyers and sellers, each with their own strategy. Those who strategize effectively are the ones rewarded. Jumping into a trade without a well-thought-out plan rarely leads to consistent success.
It’s crucial to learn different strategies so that you can adapt to various market situations. But more importantly, you must take the step of writing down your trading plan. Determine when to enter and exit a trade, when and how you will manage it, and most importantly, stick to the plan. This discipline allows you to analyze trades afterward and improve your strategies over time, making you a better trader.
Trading Too Big
We’ve all been tempted to go all-in at some point—betting everything on a single trade, hoping for a big win. However, this approach is extremely risky and often leads to significant losses.
If you’ve made this mistake, chances are you’ve quickly learned the hard way. Risk management is crucial in options trading. Instead of putting everything on the line, trade with a size that aligns with your risk tolerance and overall investment strategy.
Options trading is a powerful tool for investors looking to profit in both rising and falling markets. By understanding various options strategies and risk management techniques, traders can generate consistent profits regardless of market conditions. This article explores how to trade options successfully and maximize returns in any market.
Understanding Options Trading
Options are derivative contracts that give traders the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price within a specified timeframe. There are two main types of options:
- Call Options: Give the holder the right to buy an asset at a set price before expiration.
- Put Options: Give the holder the right to sell an asset at a set price before expiration.
Traders can use various strategies to profit from market movements, volatility, and even stagnation.
Profiting in a Bullish Market
1. Buying Call Options
One of the simplest ways to profit in a bullish market is to buy call options. This strategy allows traders to benefit from upward price movements without needing to invest the full price of the asset.
- Example: If a stock is trading at $50 and a trader buys a call option with a $55 strike price, they profit if the stock price exceeds $55 before expiration.
2. Selling Put Options
Selling put options allows traders to collect premiums while expecting the stock price to remain above the strike price. This strategy works well in bullish or neutral markets.
- Example: A trader sells a put option with a $45 strike price on a stock trading at $50. If the stock remains above $45, the trader keeps the premium.
3. Bull Call Spread
A bull call spread involves buying a lower strike call option and selling a higher strike call option simultaneously. This strategy reduces cost while maintaining potential profits.
- Example: Buy a $50 call option and sell a $55 call option. If the stock rises above $55, the maximum profit is realized.
Profiting in a Bearish Market
1. Buying Put Options
Buying put options is a straightforward way to profit in a declining market. As the asset’s price falls, the value of the put option increases.
- Example: A trader buys a put option with a $60 strike price on a stock trading at $65. If the stock price drops to $50, the put option gains value.
2. Selling Call Options
Selling call options can generate income if the stock price remains below the strike price. Traders collect premiums but take on the risk of stock appreciation.
- Example: A trader sells a call option with a $70 strike price. If the stock remains below $70, they keep the premium.
3. Bear Put Spread
A bear put spread involves buying a put option at a higher strike price and selling another put at a lower strike price, limiting potential losses.
- Example: Buy a $60 put option and sell a $55 put option. If the stock drops below $55, maximum profit is realized.
Profiting in a Neutral Market
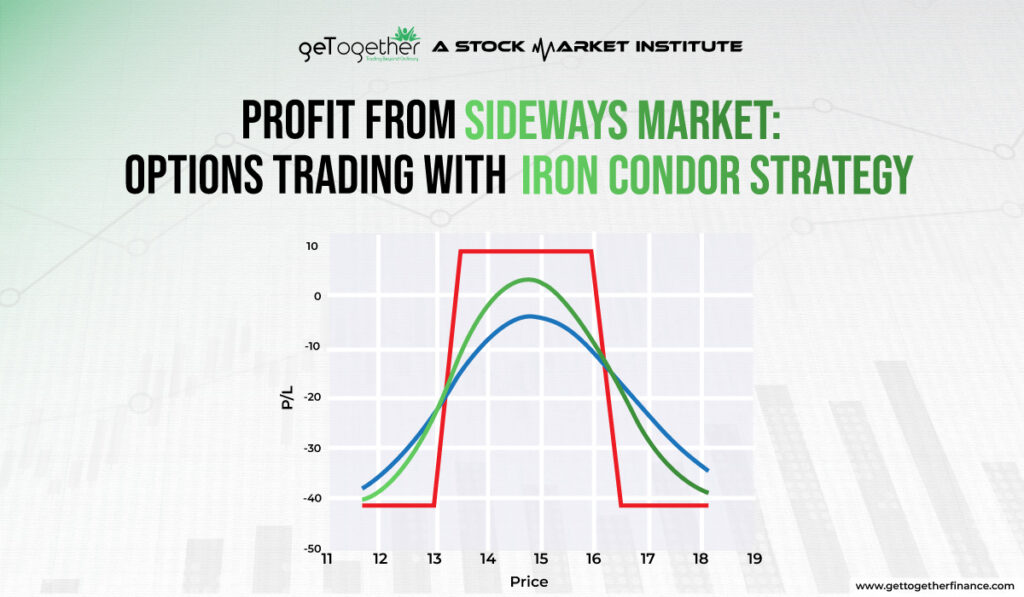
1. Selling Iron Condors
An iron condor involves selling both a call spread and a put spread on the same asset. This strategy profits when the stock price remains within a set range.
- Example: Sell a $50 put, buy a $45 put, sell a $70 call, and buy a $75 call. If the stock stays between $50 and $70, the trader keeps the premium.
2. Using Straddles and Strangles
These strategies involve buying both call and put options simultaneously to profit from significant price movements in either direction.
- Example: If a stock is at $100, a trader buys a $100 call and a $100 put. If the stock moves significantly up or down, profits are made.
Risk Management in Options Trading
1. Position Sizing
Traders should only risk a small portion of their capital on each trade to manage losses effectively.
2. Setting Stop Losses
Using stop losses prevents excessive losses by automatically closing a position if it moves against the trader.
3. Hedging Strategies
Traders can use options to hedge existing stock positions and reduce potential losses.
- Example: A trader holding 100 shares of a stock can buy a put option to protect against a downturn.
Conclusion
Options trading offers numerous opportunities to profit in any market condition. By using the right strategies and managing risks effectively, traders can capitalize on bullish, bearish, and neutral trends. Whether buying calls in a rally, purchasing puts in a decline, or deploying neutral strategies, mastering options trading can significantly enhance profitability. However, traders must remain disciplined, continuously educate themselves, and implement risk management to succeed in the long run.